Immunoassays are a set of biochemical techniques that are used to detect or quantify a certain molecule through an immunological reaction. The main basis shared by all immunoassays is that they are based on antigen-antibody avidity.
Apart from serving for the detection of molecules in the laboratory, they are used in the field of medicine for the diagnosis of multiple diseases. In this post we briefly review the 9 types of immunoassays that are most frequently carried out in research laboratories.
At Abyntek Biopharma we have an extensive catalogue with more than 7 million references.
Contact us and we will advise you on which are the best kits or reagents to carry out your experiment.
TYPES OF IMMUNOASSAYS
1.- WESTERN BLOT (WB)
Using the Western Blot technique, the proteins present in a given biological sample are separated based on their size by electrophoresis, to later be transferred to a membrane and stained with a specific antibody.
With this technique, in addition to detecting the protein of interest, its size can be determined, confirm if there are post-translational modifications or compare its concentration in different samples, among others.
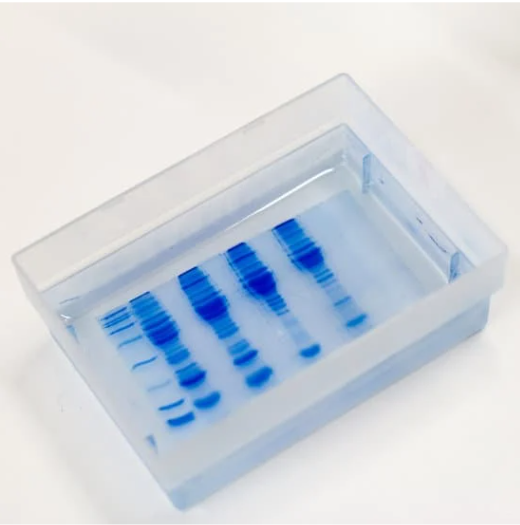
2.- ImMUNOPRECIPITAtion (IP)
Immunoprecipitation is used to isolate a certain protein from the rest of the components present in a sample, through the precipitation of antigen-antibody complexes.
In addition to the detection and quantification of proteins, its applications are very varied, including the determination of the molecular weight of a certain antigen, the study of interactions between proteins or the monitoring of post-translational modifications.
3.- RADIOImmunoassay (RIA)
This immunoassay uses radioactive isotopes to label the antigen-antibody complex. Subsequently, the radioactivity is read to detect the complexes and confirm and quantify the presence of the protein of interest in the sample.
One of the advantages of the Radioimmunoassay is that it is a highly sensitive technique, which makes it possible to detect proteins that are found at very low concentrations in the sample. However, it also has a major handicap, and it is the potential danger of working with radioactive material.
4.- ELISA (enzyme immunoassays)
Of the different types of immunoassays, the ELISA is one of the most popular and most frequently used in research laboratories due to its easy implementation, its versality, and its high sensitivity and specifity.
It is based on the use of enzymes that will allow the detection of antigen-antibody junctions (and therefore the presence of a certain antigen in the sample) by catalysing a colorimetric reaction by adding the corresponding substrate.
5.- CLIA (CHEMILUMINISCENCE IMMUNOASSAYS)
Chemiluminescence assays or CLIA share a principle with ELISA, with the difference that in this case the antigen-antibody binding is measured through the fluorescence generated by a chemical reaction.
CLIA assays have the disadvantage that they require specific equipment to read fluorescence, but on the other hand, they have the advantage of being significantly more sensitive than conventional ELISAs.
6.- ImMUNOFLUOrescence (IF)
In immunofluorescence assays, the detection of the antigen of interest through its binding to a specific antibody is visualized through the use of fluorophores.
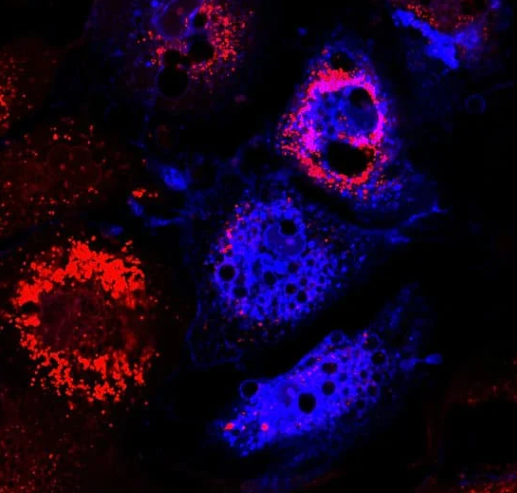
7.- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
This assay combines immunological, biochemical and histological techniques for the detection of an antigen present in a section of tissue through the use of specific antibodies. In addition, it allows visualizing the distribution and location of the antigen within the tissue under study.
8.- Immunocytochemistry(ICC)
It is a technique with a similar basis to immunohistochemistry, only that, in this case, immunocytochemistry allows the detection of an antigen within a cell. Both IHC and ICC are somewhat fewer sensitive assays than an ELISA or a Western Blot can be, but they allow the antigen to be studied in the context of an intact cell or tissue, without the need to previously isolate it.
9.- Flow citometry (FC)
Within the different types of immunoassays, this is one of the most complex. Flow cytometry is a method that measures the dispersion and reflection of a laser light beam to count and analyse cells in suspension based on their physicochemical characteristics.
Do you know our research reagents search engine?
In our search engine you can easily identify the products that best suit your research and directly request the price and technical data sheet.
Find out now!